Ohio's Agricultural Symphony: Decoding the Planting Season
Is there anything more thrilling than witnessing the earth wake up after a long winter's nap? In Ohio, that awakening takes the form of planting season, a ritual as ingrained in the state's identity as buckeye candies and football Saturdays. This isn't just about throwing seeds in the ground; it's a carefully orchestrated ballet of timing, climate, and tradition.
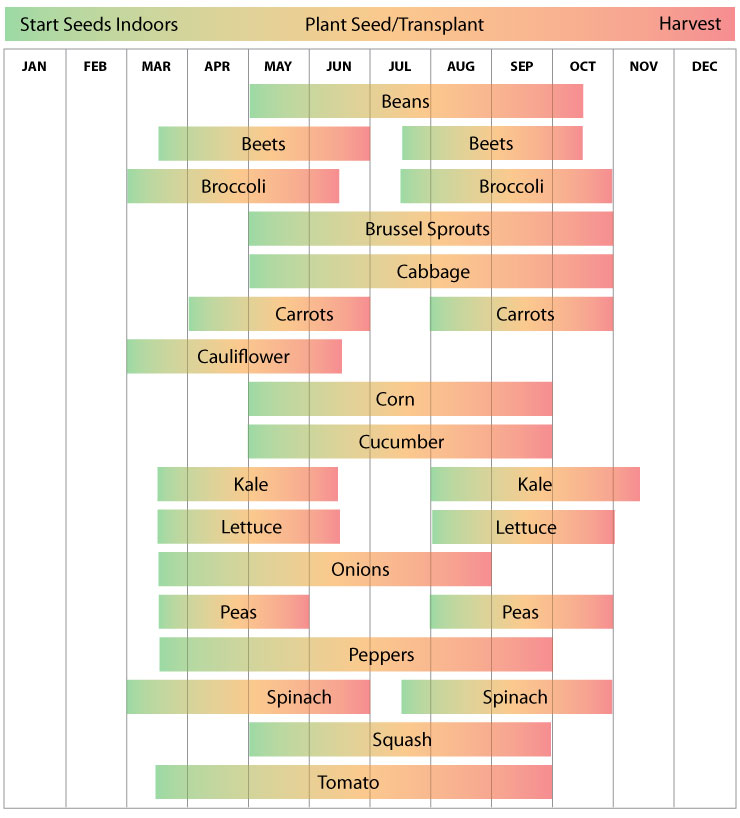
Ohio's planting season isn't a monolithic event. It's a staggered, nuanced dance determined by the last frost date, soil temperature, and the specific crop being sown. Think of it as a carefully curated playlist, with each plant having its preferred debut moment. Early spring sees the hardy souls like peas and lettuce bravely taking the stage, followed by the warmer-weather divas like tomatoes and peppers. Understanding this rhythm is key to a bountiful harvest.
The agricultural history of Ohio is deeply entwined with its planting seasons. From the indigenous peoples who cultivated crops like corn and beans to the waves of settlers who transformed the landscape into a breadbasket, the timing of planting has always been paramount. This historical perspective provides context for the current practices and underscores the importance of adapting to changing climates and evolving agricultural needs.
The ideal Ohio planting calendar is a moving target, influenced by the unpredictable whims of Mother Nature. The "frost-free" date, a benchmark for many gardeners, is a guideline, not a guarantee. Microclimates, elevation, and even urban heat islands can shift the optimal planting window. This delicate balance makes staying informed about local conditions crucial for success.
Understanding the optimal planting times for different crops is like knowing the dress code for a party. Planting too early risks exposing tender seedlings to frost damage, while planting too late can mean a shortened growing season and reduced yields. Resources like the Ohio State University Extension provide invaluable information on recommended planting dates and best practices tailored to the state's unique climate.
One of the primary benefits of a well-timed planting season is maximized yield. Getting crops in the ground at the right moment allows them to take full advantage of the growing season, resulting in healthier plants and a more abundant harvest. This is especially important for commercial growers, where timing directly impacts profitability.
Another advantage is improved crop quality. Plants grown under optimal conditions are less susceptible to disease and pests, leading to higher-quality produce. This translates to better flavor, texture, and nutritional value, whether you're selling at a farmer's market or enjoying the fruits (and vegetables) of your labor at home.
A successful Ohio planting season contributes to food security, both on a local and regional level. By maximizing yields and ensuring crop quality, Ohio's farmers play a vital role in feeding communities within the state and beyond.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ohio's Planting Season
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Long growing season for certain crops | Unpredictable weather patterns, including late frosts and early heat waves |
| Fertile soil in many regions | Potential for pest and disease pressure due to humidity |
| Abundant rainfall in some areas | Risk of flooding in certain regions |
Best Practices for Planting in Ohio:
1. Soil Testing: Know your soil's pH and nutrient levels.
2. Seed Starting Indoors: Get a head start on warm-season crops.
3. Hardening Off Seedlings: Gradually acclimate seedlings to outdoor conditions.
4. Proper Spacing: Give plants room to thrive.
5. Watering Wisely: Provide consistent moisture without overwatering.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. When should I plant tomatoes in Ohio? Typically after the last frost, around mid-May.
2. What are good cool-season crops for Ohio? Lettuce, spinach, peas, and radishes.
3. How can I protect my plants from frost? Use row covers or cloches.
4. When is the best time to plant corn in Ohio? Late April to early May.
5. What are common garden pests in Ohio? Aphids, slugs, and Japanese beetles.
6. How can I improve my soil for planting? Add compost or other organic matter.
7. Where can I find information on Ohio planting dates? The Ohio State University Extension.
8. What are some good companion planting combinations? Tomatoes and basil, carrots and onions.
Tips and Tricks: Consider succession planting for a continuous harvest. Utilize raised beds for better drainage and soil control. Implement pest control methods early to prevent infestations.
The Ohio planting season is more than just an agricultural practice; it's a testament to the state's enduring connection to the land. From the first seeds sown in spring to the final harvest in autumn, it's a cycle that sustains communities and nourishes both body and soul. By understanding the nuances of Ohio's unique climate and embracing best practices, gardeners and farmers alike can participate in this timeless tradition and reap the rewards of a bountiful harvest. Whether you're a seasoned farmer or a backyard enthusiast, taking the time to plan and prepare for the planting season is an investment that pays dividends in fresh, local produce and a deeper appreciation for the rhythms of nature. So, get your hands dirty, embrace the challenges, and celebrate the abundance that Ohio's planting season has to offer.
Magical ink exploring harry potter tattoo ideas for men
Upgrade your romance game sweet nothings for your girlfriend
Conquering the road your guide to a pre owned gmc 2500 duramax at4






/zone-map-north-east-big-5692a5b83df78cafda81dd81.jpg)