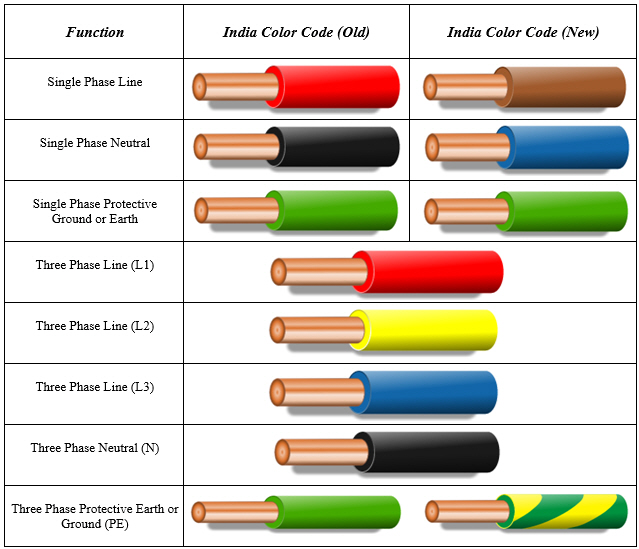
Decoding the Green-Yellow Stripe: Your Guide to Ground Wires
Ever noticed that distinctive green wire with a yellow stripe snaking through your electrical system? It's not there for decoration. That unassuming conductor plays a vital role in keeping you, your home, and your electronics safe from potentially dangerous electrical faults. Understanding its function is crucial for anyone dealing with electricity, whether you're a seasoned electrician or a curious homeowner.
This vibrant green-and-yellow cable is the unsung hero of electrical safety, providing a low-resistance path for stray currents to flow safely into the earth. Without it, a faulty appliance could energize its metal casing, turning a seemingly harmless object into a shock hazard. The green-yellow ground wire acts as an escape route for this dangerous electricity, preventing it from harming you or your equipment.
The concept of grounding dates back to the early days of electricity, evolving alongside our understanding of electrical safety. Early electrical systems lacked dedicated grounding, leading to numerous accidents and the recognition of the need for a protective mechanism. The introduction of the green-yellow striped ground conductor marked a significant leap forward in electrical safety standards, dramatically reducing the risk of electric shocks.
The importance of a properly installed and maintained grounding conductor cannot be overstated. It serves as the foundation of a safe electrical environment, protecting against faults, surges, and other electrical anomalies. This safety feature is internationally recognized, with the green-yellow color coding standardized to ensure consistent identification across various electrical systems.
The principle behind a green and yellow striped earth wire is simple yet effective. It provides a dedicated pathway for fault currents to flow to the ground, bypassing the normal circuit path. This rapid diversion of current triggers protective devices like circuit breakers or fuses, swiftly shutting off the power and preventing further damage or injury. This prompt action minimizes the risk of electrical fires and protects connected equipment from voltage spikes.
One of the key benefits of a properly functioning ground system is the protection it offers against electric shock. By providing a low-resistance path to ground, it prevents dangerous voltages from building up on conductive surfaces. This crucial function safeguards individuals from potentially lethal shocks.
Another advantage is the protection of sensitive electronic equipment. Grounding helps to dissipate static electricity and transient voltages, which can damage or destroy electronic components. This is particularly important in today's world, where we rely heavily on delicate electronic devices.
A third benefit is the stabilization of voltage levels within the electrical system. The ground connection acts as a reference point, helping to maintain consistent voltage levels and prevent fluctuations that can harm equipment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Properly Grounded Systems
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Protection from electric shock | Cost of installation (for retrofits) |
| Protection of electronic equipment | Requires periodic inspection |
| Voltage stabilization | Can be complex in older buildings |
Best Practices for Grounding:
1. Ensure all metal enclosures are bonded to the ground wire.
2. Use proper connectors and ensure tight connections.
3. Periodically inspect the grounding system for damage or corrosion.
4. Use the correct gauge of ground wire for the application.
5. Consult a qualified electrician for complex grounding situations.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What does the green-yellow stripe signify? - It indicates a ground wire.
2. Why is grounding important? - It protects against electric shock and equipment damage.
3. Can I use a different colored wire for grounding? - No, the green-yellow stripe is standardized.
4. What should I do if my ground wire is broken? - Contact a qualified electrician immediately.
5. How often should I inspect my grounding system? - At least annually.
6. What is the difference between grounding and bonding? - Bonding connects conductive parts to equalize potential, while grounding connects to earth.
7. Can I ground my system myself? - Basic grounding can be done DIY, but consult an electrician for complex systems.
8. What are some signs of a grounding problem? - Frequent tripping of circuit breakers, tingling sensation when touching appliances, or flickering lights.
In conclusion, the seemingly simple green-yellow striped ground wire is a critical component of any electrical system. Its function extends far beyond mere compliance with regulations; it forms the bedrock of electrical safety, protecting lives and property from the potentially devastating consequences of electrical faults. Understanding its role, adhering to best practices, and ensuring regular maintenance are essential for everyone interacting with electrical systems. By prioritizing proper grounding, we contribute to a safer and more secure electrical environment for ourselves and our communities. Don't underestimate the importance of this unassuming safety hero – it might just save your life.
The art of the heartfelt birthday letter to your best friend
Unlocking your paycheck a guide to cara kira gaji kilang
Bridging borders where is reynosa located and why is it a tech hub on the rise