Decoding the Enigma: Understanding Your Car's Engine Codes
That little amber glow on your dashboard – the check engine light – can be a source of both mild annoyance and full-blown panic. What does it mean? Is your car about to explode? Probably not, but ignoring it is akin to dismissing a persistent cough. Understanding engine trouble codes is crucial for every car owner, empowering you to take control of your vehicle's health and potentially avoid costly repairs down the line. This guide will illuminate the often-confusing world of engine diagnostic codes, providing you with the knowledge to navigate car troubles with confidence.
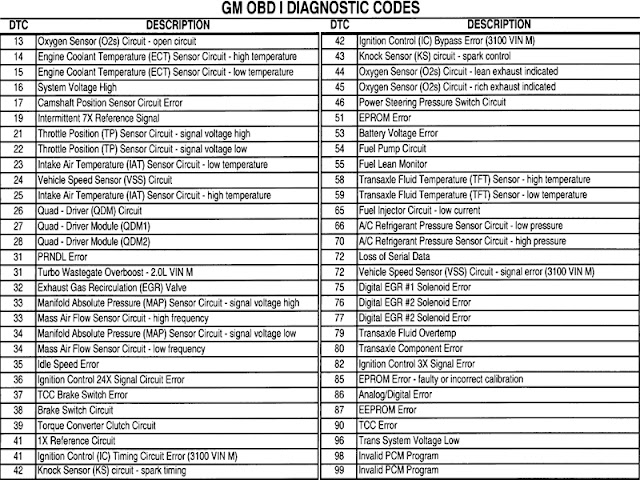
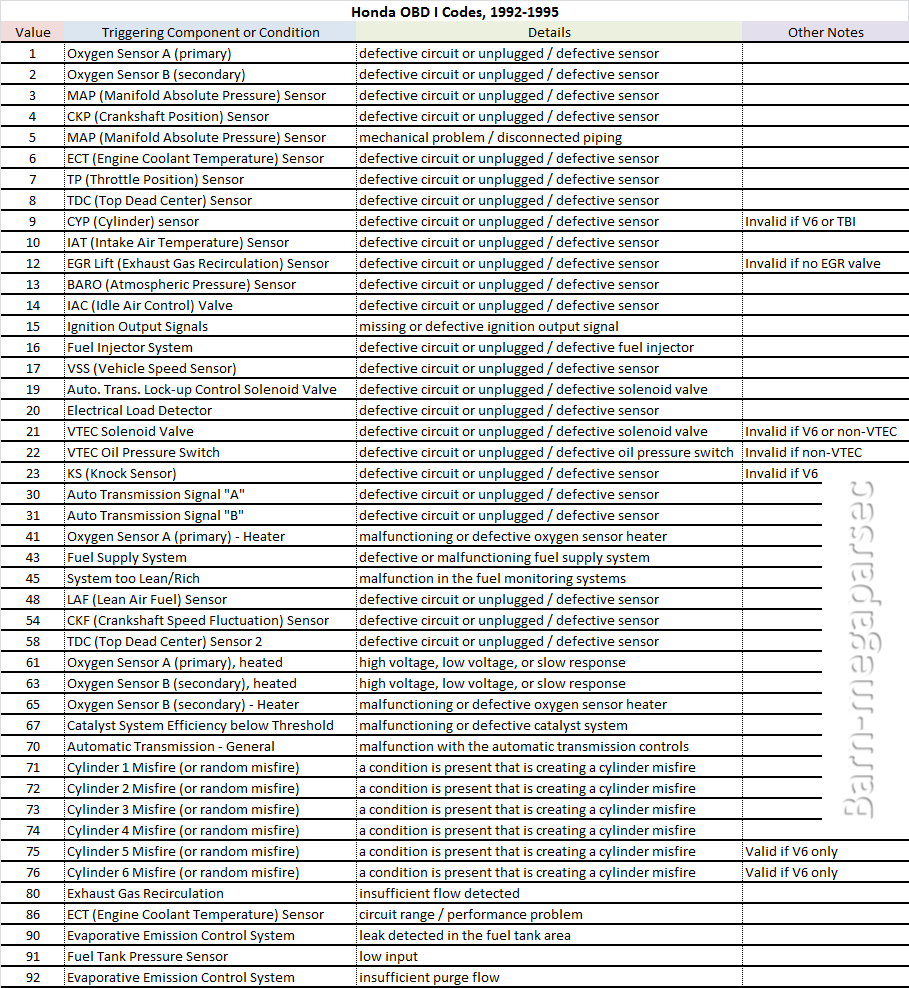
Imagine your car's onboard computer as a constantly vigilant physician, monitoring every heartbeat, breath, and twitch of your engine. When something goes awry, it logs the issue as a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), commonly referred to as an engine code. These codes are the key to understanding what's happening under the hood. While the check engine light itself serves as a general warning, the specific code reveals the nature of the problem.
The standardization of engine diagnostic codes emerged in the 1980s, initially driven by regulations aimed at reducing emissions. Over time, these codes evolved into a comprehensive system encompassing a vast range of potential issues, from minor sensor malfunctions to serious engine problems. Before standardized codes, diagnosing car problems often involved a laborious process of elimination, requiring significant time and expertise. The introduction of these codes revolutionized automotive diagnostics, making it easier and more efficient to pinpoint problems.
The importance of promptly addressing engine codes cannot be overstated. A seemingly minor issue, if left unchecked, can escalate into a major and expensive repair. For example, a faulty oxygen sensor might initially only impact fuel efficiency, but over time, it can damage the catalytic converter, a costly component to replace. By understanding and addressing engine codes early, you can save yourself from significant financial headaches.
One of the main issues related to checking engine codes is misinterpretation. While accessing the codes themselves is relatively straightforward with an OBD-II scanner, understanding what they mean requires some research. Simply clearing the code without addressing the underlying issue is like silencing a fire alarm without putting out the fire – the problem will likely resurface, and potentially with more serious consequences.
Accessing engine codes typically involves using an OBD-II scanner, a readily available device that plugs into your car's diagnostic port. Once connected, the scanner can retrieve the stored codes, which are typically formatted as a combination of letters and numbers (e.g., P0420, which indicates a catalytic converter issue). Numerous online resources and apps can help you decipher these codes and understand their potential causes.
One benefit of promptly checking engine codes is early problem detection. This allows you to address issues before they escalate, saving money on repairs. Another benefit is improved fuel efficiency. Some engine problems, such as faulty oxygen sensors, can negatively impact fuel economy. Addressing these issues can lead to better mileage. Finally, regular code checks contribute to the overall longevity of your vehicle by ensuring that problems are identified and addressed promptly, preventing long-term damage.
Here’s a simple action plan: 1. Observe the check engine light. 2. Retrieve the code with an OBD-II scanner. 3. Research the code. 4. Determine the necessary action. 5. Address the underlying issue or consult a mechanic.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Engine Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Early problem detection | Potential for misinterpretation |
| Improved fuel efficiency | Codes may not pinpoint the exact problem |
| Cost savings on repairs | Requires a diagnostic tool (OBD-II scanner) |
Best practice: Don't ignore the check engine light. Regularly check for codes even without a lit light. Research codes thoroughly before taking action. Address underlying issues promptly. Consult a qualified mechanic if needed.
Example: A P0300 code indicates a random misfire. This could be caused by spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors. A P0420 code suggests a catalytic converter problem. A P0171 code might indicate a lean air/fuel mixture.
FAQ: What does the check engine light mean? How do I check engine codes? What is an OBD-II scanner? Can I drive with the check engine light on? How much does it cost to fix an engine code? What are the most common engine codes? What does a flashing check engine light indicate? How do I clear engine codes?
In conclusion, understanding and addressing engine codes is an essential part of responsible car ownership. By familiarizing yourself with this diagnostic system, you can empower yourself to take control of your vehicle's maintenance, prevent costly repairs, and extend the life of your car. The check engine light, while sometimes unsettling, is not something to fear. It's a valuable tool that provides insights into your car's health. Don't ignore it – decipher its message, take appropriate action, and keep your car running smoothly for years to come. Remember that a little knowledge can go a long way in saving you time, money, and frustration on the road.
Supercharge your essays unleashing the power of transition words
From vision to ink the power of stencil outline tattoo drawings
The colorful world of rainbow friends desenho animado