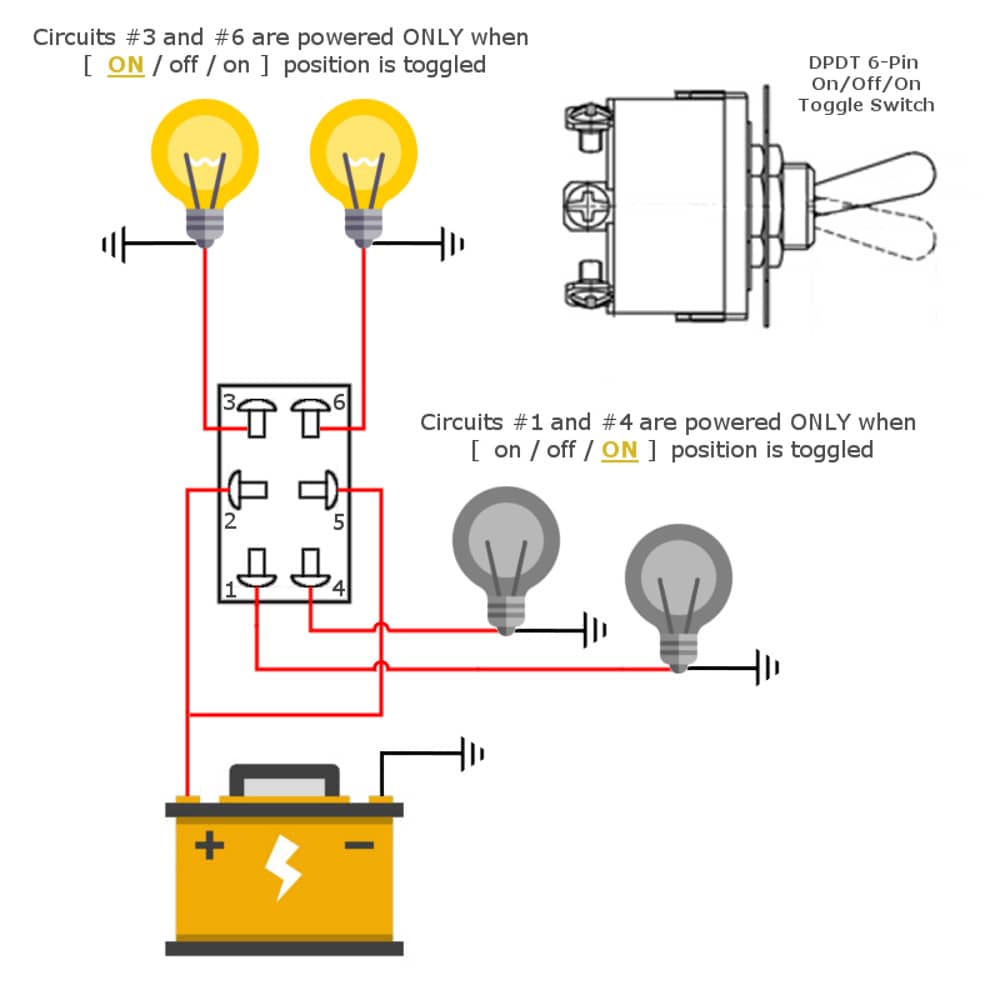
Decoding the DPDT On-Off-On Rocker Switch
Ever wondered how a single switch can control two separate circuits simultaneously? The double-pole, double-throw (DPDT) on-off-on rocker switch is the unsung hero behind this functionality, offering a versatile control mechanism for a wide range of applications. This seemingly simple component packs a powerful punch, enabling complex circuit configurations with a satisfying click.
The DPDT on-off-on rocker switch is a type of electrical switch that allows users to control two separate circuits with a single actuator. Its three-position design – on, off, and on – offers unique control capabilities, making it a staple in various electronic devices and systems. This article dives deep into the world of DPDT on-off-on rocker switches, exploring their functionality, applications, benefits, and best practices.
The origin of the DPDT switch can be traced back to the early days of electrical engineering, alongside the development of other fundamental switching mechanisms. As electrical systems became more complex, the need for controlling multiple circuits with a single switch arose, leading to the innovation of the DPDT design. Its importance lies in its ability to simplify complex wiring setups and provide flexible control options.
A common issue with DPDT rocker switches, like any mechanical component, is wear and tear over time. Repeated switching can lead to contact degradation, resulting in intermittent connections or complete switch failure. Choosing high-quality switches and ensuring proper installation are crucial to mitigating these issues.
Understanding the terminology associated with DPDT switches is essential for effective implementation. "Double-pole" refers to the switch's ability to control two separate circuits simultaneously. "Double-throw" indicates that each pole has two possible contact positions. The "on-off-on" designation signifies the three stable positions of the rocker actuator, allowing for various circuit configurations.
One benefit of using a DPDT on-off-on rocker switch is its versatility in controlling two separate circuits. For example, in a lighting application, it can be used to switch between two different light sources or control a light fixture from two separate locations. Another advantage is its compact size, making it suitable for space-constrained applications. Lastly, its simple operation makes it user-friendly, even for those with limited technical expertise.
Implementing a DPDT on-off-on rocker switch successfully involves careful planning and execution. Begin by understanding the circuit requirements and selecting the appropriate switch rating. Next, carefully wire the switch according to the circuit diagram, ensuring proper connections for each pole and throw. Finally, test the circuit thoroughly to verify correct operation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DPDT On-Off-On Rocker Switches
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Versatile control of two circuits | Potential for contact wear over time |
| Compact size | Can be more complex to wire than simpler switches |
| User-friendly operation | Higher cost compared to single-pole switches |
Best practices for implementing DPDT switches include using the correct wire gauge for the application, ensuring secure connections to prevent loose wires, and using a wiring diagram specific to the switch and circuit. Additionally, choosing a switch with a suitable current and voltage rating is critical for safe and reliable operation.
One real-world example is using a DPDT switch to control a ceiling fan with separate switches for the fan motor and the light. Another example is in automotive applications, where a DPDT switch can control both the high and low beams of headlights.
A common challenge is miswiring the switch, leading to incorrect circuit operation. The solution is to carefully follow the wiring diagram and double-check connections. Another challenge is selecting the wrong switch rating, which can lead to overheating or even fire. The solution is to carefully calculate the current and voltage requirements of the circuit and choose a switch with an appropriate rating.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about DPDT switches often include inquiries about wiring diagrams, switch ratings, and common applications.
Tips and tricks for working with DPDT rocker switches include using a multimeter to test the switch's functionality and using wire labels to clearly identify each connection.
In conclusion, the DPDT on-off-on rocker switch is a versatile and essential component in numerous electrical and electronic systems. Its ability to control two independent circuits with a single actuator simplifies complex wiring setups and provides flexible control options. From controlling lighting fixtures to managing complex industrial machinery, the DPDT switch plays a crucial role. By understanding its functionality, benefits, and best practices for implementation, users can harness its power to create efficient and reliable control systems. While challenges such as wear and tear and potential miswiring exist, careful planning and adherence to best practices can mitigate these issues. The versatility and compact design of the DPDT on-off-on rocker switch make it a valuable component for any electronics enthusiast or professional. Its ability to streamline complex circuits and provide user-friendly control continues to make it a staple in modern technology.
Powerful ink exploring native american tribal tattoos for men
Unlocking language the power of kindergarten worksheets english alphabet
Navigating calhoun county commission alabama